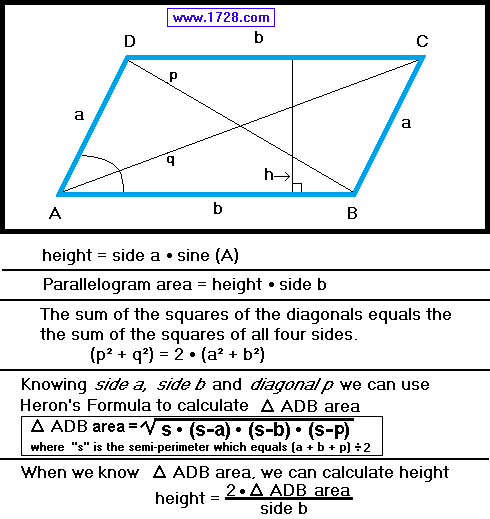
Parallelogram area = (height × AB) or (height × DC)
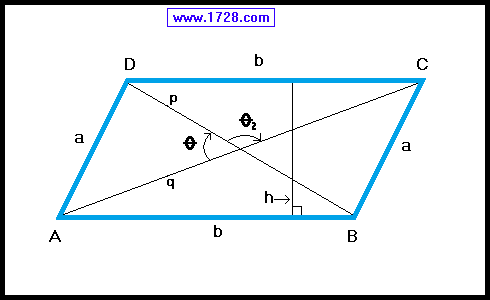
Lines AC and DB are called diagonals.
Diagonals bisect each other.
Diagonals are not equal.
Diagonals do not bisect the vertex angles.
Line 'h' is perpendicular to lines AB & DC and is
called the height or altitude.
• BOTH pairs of opposite sides are equal.
AB = DC and AD = BC
• BOTH pairs of opposite angles are equal.
∠ A = ∠ C and ∠ B = ∠ D
• Adjacent angles are supplementary.
∠ A + ∠ D = ∠ D + ∠ C = ∠ C + ∠ B = ∠ B + ∠ A = 180°
• Each diagonal forms 2 congruent triangles.
Δ ADC = Δ ABC and Δ DAB = Δ DCB
The default setting is for 5 significant figures but you can change that
by inputting another number in the box above.
Answers are displayed in scientific notation and for easier readability, numbers between
.001 and 1,000 will be displayed in standard format (with the same number of
significant figures.)
The answers should display properly but there are a few browsers that will show
no output whatsoever. If so, enter a zero
in the box above. This eliminates all formatting but it is better than seeing no
output at all.